Everyday Plastic You Encounter — But Do You Really Understand It?Have you ever noticed a small tria...
Injection molding process and problem analysis
Injection molding is one of the most commonly used methods in the plastic processing industry, widely applied in the manufacturing of various plastic products. The principle is to heat the plastic raw material to a molten state, inject the molten plastic into a mold using an injection molding machine, and after cooling and solidification, obtain the desired plastic components. Below is a detailed introduction to the injection molding process and an analysis of common issues:

1. Rubber Injection Molding
Rubber injection molding is a process where rubber material (usually thermosetting rubber) is directly injected into a mold using an injection molding machine and vulcanized. The key features and advantages are as follows:
· High production efficiency: Compared to traditional manual or compression molding, rubber injection molding can significantly improve production efficiency, especially in large-scale production.
· No need for pre-material preparation: This process does not require pre-treatment of rubber (such as preheating or preforming), reducing time and labor intensity.
· Excellent product quality: Due to the use of precise mold design and injection process control, the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of the products are relatively high.
· Applications: Widely used in industries such as automotive, electronics, and medical fields, producing various seals, gaskets, washers, and rubber components.
2. Plastic Injection Molding
Plastic injection molding is the most commonly used industrial molding process, particularly suitable for thermoplastic materials. The process involves injecting molten plastic into a mold and cooling it to obtain the required plastic products. Key characteristics include:
· Wide range of applications: Commonly used plastic materials include polyester (PA), polypropylene (PP), polystyrene (ABS), and others, which offer good formability, low cost, and recyclability.
· Injection molding machine: The plastic injection molding machine varies according to material properties, product complexity, and molding precision requirements. Common types include vertical, horizontal, and fully electric machines.
· Product variety: Plastic injection molding can produce a wide range of products, from small electronic components to large automotive parts, and can integrate complex geometric structures such as threads, holes, ribs, etc.
· High efficiency: The molding cycle is relatively short, allowing for rapid production of large quantities of products, especially suitable for precision plastic parts.
· Precision and appearance: Injection molding can provide high dimensional accuracy and good appearance quality, making it the preferred molding method for many industries.
3. Molding Injection Molding
Molding injection molding refers to the process of directly obtaining the final product shape through the injection molding process without requiring further processing or post-treatment. Compared to traditional processes such as compression molding or casting, injection molding has the following features:
· Integrated molding: In the injection molding process, many design details such as recesses, ribs, and threads can be directly formed, reducing subsequent processing steps.
· Complexity of parts: Many complex shapes and fine details can be completed during the injection molding process, avoiding additional steps.
· Efficient production: Injection molding is an efficient and automated process suitable for mass production, especially for precision parts, achieving very high dimensional and shape accuracy.
· Material saving: In injection molding, material flow can be precisely controlled, reducing waste, and the molded products generally have good structural strength.
4. Other Classifications of Injection Molding
· Compression molding and die-casting: In addition to traditional injection molding, compression molding and die-casting also have unique advantages when processing different materials and products. Compression molding is mainly used for molding polymer rubber and thermosetting plastics, while die-casting is mainly used for casting metal materials.
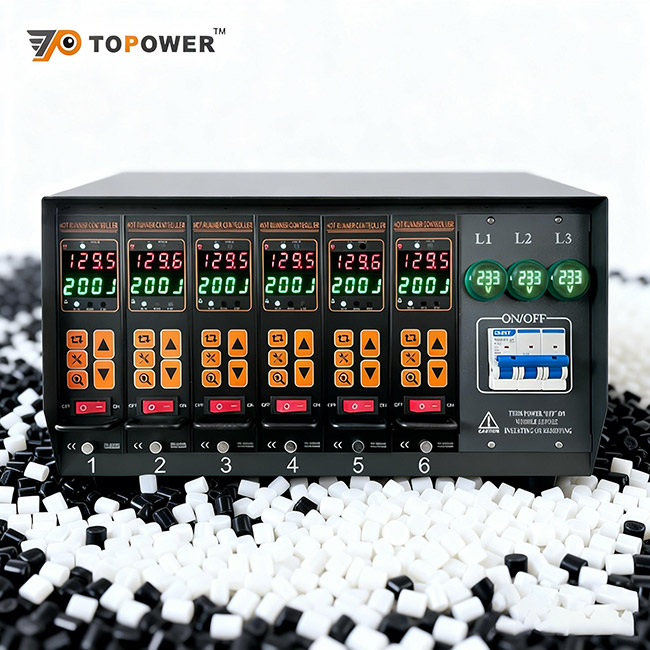
· Injection molding process control: Parameters such as temperature, pressure, and injection speed during the injection molding process directly affect product quality and production efficiency. Therefore, the design of the injection molding machine and mold must be precise to achieve optimal production results.
5. Applications of Injection Molding
Injection molding has a wide range of applications and is almost used in all manufacturing industries, including but not limited to:
· Automotive manufacturing: Producing automotive interior parts, exterior parts, seals, etc.
· Electronics industry: Manufacturing electronic enclosures, connectors, buttons, etc.
· Medical industry: Producing precision components and consumables for medical devices.
· Consumer goods: Plastic products such as household appliances, toys, and stationery.
· Packaging industry: Plastic bottles, packaging containers, etc.
Conclusion
Injection molding has broad prospects and development potential in the molding of rubber, plastic, and molding injection applications. With technological advancements and continuous material innovation, the precision, efficiency, and automation levels of injection molding processes continue to improve, providing strong support for product innovation in various industries. In practical applications, the appropriate injection molding process should be selected based on the complexity of the product, material characteristics, and production efficiency requirements.
II. Injection Molding Process Flow
1. Injection Molding Machine Preparation: Choose the appropriate injection molding machine based on the size of the mold, product requirements, and material characteristics to determine the machine specifications and parameters.
2. Material Preparation: Place plastic pellets into the hopper of the injection molding machine, ensuring the raw materials are free from impurities and meet production requirements.
3. Heating the Plastic: The plastic pellets are heated through the injection molding machine’s screw to gradually melt. This process typically involves both heating and mixing steps.
4. Injection Molding: The molten plastic is quickly injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. This process requires strict control of injection pressure, speed, and temperature.
5. Cooling and Solidification: The injected plastic gradually solidifies with the help of a cooling system to form the required shape.
6. Mold Opening and Demolding: After cooling, the mold is opened, and a demolding device extracts the molded plastic products from the mold.
7. Post-Processing: The molded products undergo cleaning, trimming, inspection, and other post-processing steps.
III. Common Types of Injection Molding
1. Thermoplastic Injection Molding: Suitable for most thermoplastic materials such as polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), and polystyrene (PS).
2. Thermosetting Plastic Injection Molding: Suitable for thermosetting plastics such as unsaturated polyester (UP) and epoxy resin (EP), which cannot be reheated or deformed after molding.
3. Co-injection (Multi-layer Injection): Multiple injection devices on the injection molding machine inject different materials into a single mold, achieving composite material effects.
4. Gas-Assisted Injection Molding: Gas (usually nitrogen) is used to apply pressure during the injection molding process, helping the plastic to fill the mold more evenly, often used for larger or thinner-walled products.
5. Extrusion Injection Molding: Heat and extrude thermoplastic materials continuously to form long, strip-shaped or tubular products.
IV. Common Issues and Solutions
Plastic Product Warping
1. Cause: Uneven cooling, poor mold design, excessive injection speed.
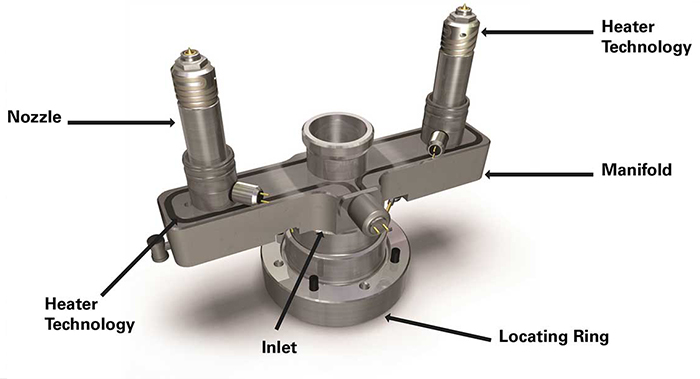
2. Solution: Optimize mold cooling system, adjust injection speed, and use heaters for even heat distribution.
Bubbles
1. Cause: Excessive moisture in raw materials, excessive injection speed or pressure.
2. Solution: Dry raw materials, adjust injection parameters, ensure proper temperature control of the barrel.
Surface Defects (e.g., Flow Marks, Gas Marks, Burn Marks)
1. Cause: Uneven mold surface, improper injection temperature, incorrect cooling time.
2. Solution: Inspect mold surface, adjust temperature and cooling time, optimize injection parameters.
Dimensional Instability
1. Cause: Poor mold size design, unstable injection pressure, poor plastic melt flow.
2. Solution: Optimize mold design, stabilize injection pressure, select suitable plastic materials.
Incomplete Filling (Cavities)
1. Cause: Low injection pressure, poor mold channel design, high plastic melt viscosity.
2. Solution: Increase injection pressure, optimize mold channel design, select suitable plastic materials.
Difficulty in Demolding
1. Cause: Poor mold design, overly smooth or rough surface.
2. Solution: Adjust mold surface treatment, increase the use of release agents.
Plastic Product Deformation
1. Cause: Too fast or too slow cooling rate, unstable injection temperature.
2. Solution: Optimize cooling system, adjust injection and cooling temperatures.
V. Injection Molding Process Optimization
To improve injection molding production efficiency and product quality, the following optimizations are generally required:
1. Mold Design Optimization: Properly design the runner system to ensure that the plastic material flows evenly into the mold cavity and reduces cooling time.
2. Material Selection and Formula Adjustment: Choose suitable plastic materials and additives based on the product’s usage requirements to avoid defects caused by material mismatches.
3. Injection Molding Machine Parameter Optimization: Adjust injection speed, pressure, temperature, and other parameters to achieve the best production effect.
4. Production Process Monitoring: Continuously monitor various data during the injection molding process and make dynamic adjustments through automated systems to ensure stable production.
VI. Conclusion
Injection molding is an efficient production method, but to ensure stable product quality, it requires detailed management and optimization from multiple aspects. Common issues can usually be resolved through adjustments in process details and equipment optimization. By continuously improving the process level, it is possible to gain a competitive advantage in the market.