Everyday Plastic You Encounter — But Do You Really Understand It?Have you ever noticed a small tria...
Injection Molding Efficiency with Hot Runner Design
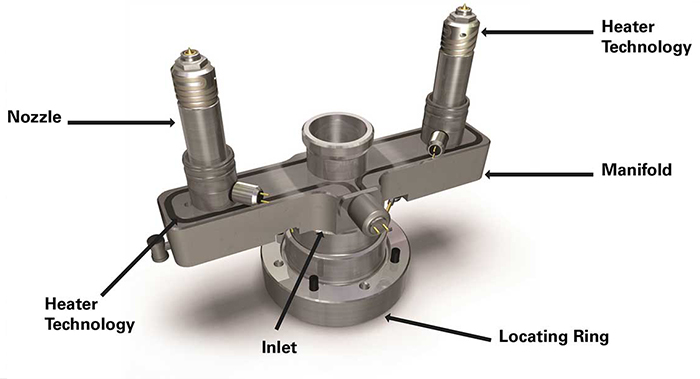
What Is a Hot Runner System?
Hot runner technology is a key innovation in modern injection molding, allowing molten plastic to flow directly from the injection molding machine into the mold cavity without producing waste from cold runners. A hot runner system typically consists of a manifold, hot nozzles, heating elements, and a temperature controller. When properly designed, it can significantly improve production efficiency, reduce material waste, and enhance part quality and consistency.
Key Principles of Hot Runner Design
1. Material Properties
Melt temperature: Different thermoplastics require different processing temperatures. Material thermal stability must be considered during design.
Flow characteristics: Highly viscous materials need larger runner diameters and shorter flow paths.
Heat sensitivity: For heat-sensitive materials, precise temperature control is essential to avoid degradation.
2. Compatibility with Mold Structure
The hot runner system must integrate seamlessly with the overall mold design.
Consider compatibility with the mold’s opening/closing mechanism and ejection system.
Adequate space should be reserved for installation and future maintenance of hot runner components.
3. Thermal Balance
Ensure even temperature distribution throughout the system.
Use properly positioned heating elements and thermocouples.
Account for thermal expansion in system layout and design.
Step-by-Step Hot Runner System Design Process
Step 1: Product and Process Analysis
Analyze product structure, dimensions, and required tolerance.
Determine cavity count and mold layout.
Evaluate production volume, cycle time, and material type.
Step 2: Hot Runner Layout Planning
Select the appropriate hot runner type (open gate, valve gate, etc.).
Design the manifold layout (straight, H-type, X-type, etc.).
Determine nozzle locations and quantity based on product geometry.
Step 3: Flow and Thermal Simulation
Conduct mold flow analysis to ensure balanced cavity filling.
Calculate pressure drop and shear rate across the system.
Simulate thermal distribution and anticipate thermal expansion zones.
Step 4: Component Selection and System Design
Choose nozzles and manifolds of suitable dimensions.
Determine heating zones and power requirements.
Design insulation components and incorporate cooling where necessary.
Critical Design Considerations
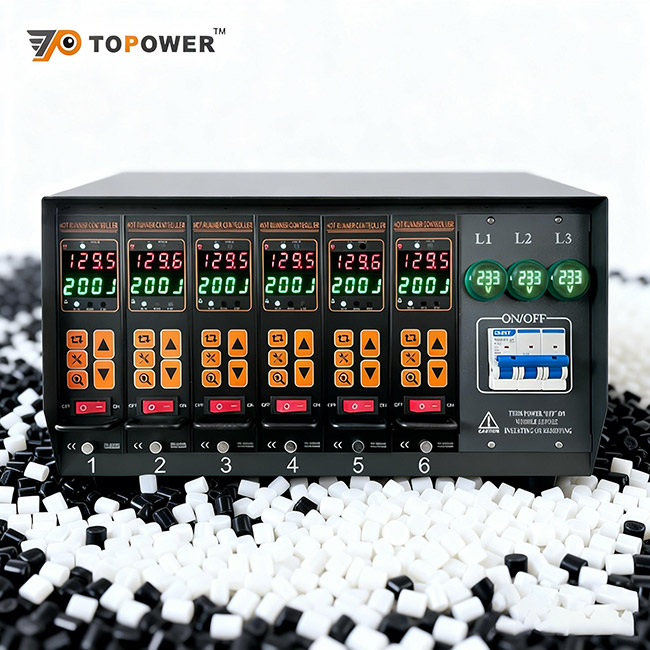
Hor runner Temperature Control
Use independent heating zones with PID controllers.
Thermocouples should be placed close to nozzle tips and manifold branches.
Maintain stable temperature profiles throughout the molding cycle.

Runner and Gate Dimensions
Main runner diameter typically ranges between 5–12 mm.
Sub-runner dimensions depend on part size and material viscosity.
Avoid abrupt cross-sectional changes to maintain consistent flow.
Thermal Expansion Management
Allow sufficient space for expansion.
Use floating manifold or nozzle connections where necessary.
Account for different thermal expansion rates of mold and hot runner materials.
Leakage Prevention
Apply proper sealing methods (e.g. conical or flat seal designs).
Ensure appropriate contact pressure.
Use high-temperature-resistant sealing materials.
Troubleshooting Common Hot Runner Issues
Maintenance Best Practices
Problem | Cause | Solution |
Drooling or stringing | Overheated nozzle tips | Use valve gates or optimize tip temperature |
Material degradation | Prolonged residence time or overheating | Control temperature, avoid dead zones |
Unbalanced filling | Inadequate runner layout | Redesign manifold flow channels or adjust temperature zones |
Leakage | Insufficient sealing or thermal stress | Use expansion joints and high-grade sealing components |
Regularly inspect heaters and thermocouples.
Clean the system during each shutdown or scheduled downtime.
Monitor and analyze temperature curve trends.
Establish a preventive maintenance program.
Future Trends in Hot Runner Technology
Smart hot runner systems with sensor integration and AI-driven diagnostics.
Energy-efficient designs with optimized heating and insulation.
Modular structures for easy maintenance and quick replacement.
Multi-material compatibility for use with composites and bioplastics.
Conclusion
By following the principles and considerations outlined in this guide, engineers and mold designers can develop efficient, stable, and high-performance hot runner systems. Proper application of hot runner technology not only enhances part quality and reduces waste, but also plays a crucial role in lowering manufacturing costs and improving overall production flexibility. As hot runner systems continue to evolve, their role in driving sustainable and intelligent injection molding will become even more essential.