Everyday Plastic You Encounter — But Do You Really Understand It?Have you ever noticed a small tria...
Hot Runner vs. Hot Gate: A Comprehensive Comparison in Injection Molding
Whether you are engaged in the injection molding industry or mold production, do you have such questions:What is the difference between hot runner and hot sprue?
The simple answer is:The hot gate is a key component of the hot runner system, and the hot runner is a complete temperature-controlled runner system covering the entire process from the injection molding machine to the cavity. Simply put: the hot runner pipe is the "entrance" and the hot gate pipe is the "entrance". The choice depends on product requirements, mold design and cost considerations.
summary
Hot runner and hot gate systems are closely related technologies in injection molding, yet they differ significantly in terms of functionality, structure, and application scenarios. This article provides a detailed comparative analysis across multiple dimensions:
1. Definition and Core Functionality
Hot Runner
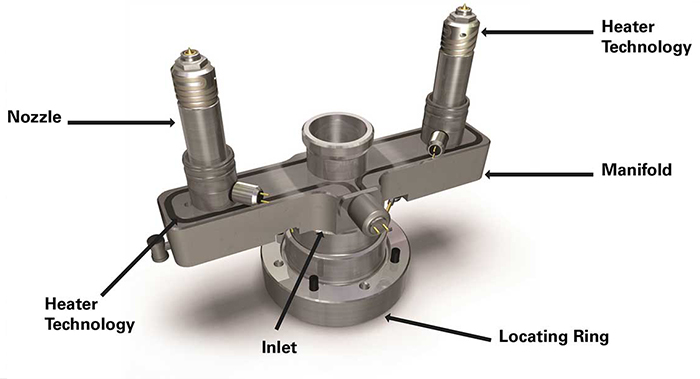
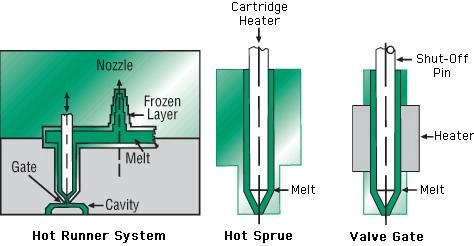
A hot runner is a complete temperature-controlled system that spans from the injection molding machine nozzle to the mold cavities. It maintains the plastic in a molten state throughout the flow path using heating elements (such as heater rods and hot runner manifolds), thereby preventing the formation of cold slugs.
Core Function: Minimize material waste and optimize the molding process.
Components: Includes hot runner manifold, nozzles (hot gate sleeves), hot runner temperature control system, and heating elements.
Types:
Single-point hot runner: A single nozzle directly injects into the cavity.
Multi-point hot runner: A manifold distributes the melt to multiple nozzles.
Hot Gate
The hot gate is the terminal execution component of the hot runner system. It specifically refers to the gate area that connects directly to the mold cavity. Localized heating ensures the plastic at the gate remains molten, preventing blockages or residue from solidified material.
Core Function: Precisely control gate temperature to ensure smooth melt flow into the cavity.
Types:
Open hot gate: Flow controlled by temperature only.
Valve gate: A mechanical valve pin regulates opening and closing.
Purpose: Prevent gate solidification and enhance the surface quality of finished products, particularly for clear or aesthetically sensitive parts.
2. Structural and Design Differences
| Dimension | Hot Runner | Hot Gate |
| System Complexity | Complex—integrates multiple components (e.g., manifold, temperature controller, heaters) and requires precise machining and thermal compensation. | Relatively simple—as the terminal part of the hot runner, only localized temperature control is needed. |
| Heating Scope | Entire flow path including the manifold and nozzles must be heated to maintain melt. | Only the gate area is heated; other sections rely on the overall temperature management of the hot runner. |
| Key Components | Manifold, temperature controller, multiple nozzles, thermal insulation layers. | Hot gate insert, valve pin (if applicable), localiz |
3. Application Scenarios
Hot Runner System :
Best suited for:
Multi-cavity molds: Even melt distribution via manifold boosts production efficiency.
High-value products: Such as transparent parts, thin-walled items, or large components requiring no gate marks or high dimensional precision.
High-volume production: Reduces cooling time and material waste, ideal for automotive, electronics, and other demanding industries.
Typical applications: Bottle caps, medical device housings, consumer electronics components.
Hot Gate
Best suited for:
Single-point injection: For precision parts in single-cavity molds, minimizing gate residue.
Appearance-critical areas: When the gate is directly on the product surface, eliminating cold slug protrusion or discoloration.
Special materials: Engineering plastics like PC or PMMA that are highly temperature-sensitive, requiring precise gate temperature control.
4. Performance and Cost Analysis
| Dimension | Hot Runner | Hot Gate |
| Cost | High initial investment (expensive components), complex maintenance (regular cleaning, heater replacement). | Lower cost as part of the hot runner system, but replacement may be limited by system integration. |
| Production Efficiency | Shorter molding cycle (no cold runner cooling time), high automation. | Improves gate filling efficiency, reduces need for additional material feeding. |
| Material Utilization | No cold runners, saving raw material (especially with high-cost plastics). | Reduces gate waste, but offers limited overall material savings. |
5. Technical Challenges and Limitations
Hot Runner
Thermal Expansion Control: Temperature differences between the manifold and the mold can cause dimensional deviation; requires precise design compensation.
Heat Loss: Long flow paths may lead to temperature gradients, affecting melt consistency.
Sealing Issues: Melt leakage may damage heating elements; strict sealing design is essential.
Hot Gate
Local Overheating Risk: Excessive temperature at the gate can degrade sensitive plastics (e.g., PVC).
Valve Pin Wear: Mechanical parts in valve gates may wear out over time and require regular maintenance.
6. Conclusion and Selection Guidelines
Essential Relationship:
The hot gate is a critical component of the hot runner system. While the hot gate focuses on localized gate temperature control, the hot runner system manages melt flow throughout the entire channel.
Selection Criteria:
Product Requirements: Opt for hot runner + valve gate for high surface quality or complex geometry.
Budget: For small-batch production, localized hot gate designs may suffice; for mass production, a full hot runner system is recommended.
Material Properties: Temperature-sensitive materials require accurate gate temperature control to avoid degradation.
Final Thoughts:
The synergistic use of hot runner and hot gate technologies can greatly enhance injection molding efficiency and product quality. However, the choice between them should be made based on a comprehensive evaluation of technical, economic, and production needs.