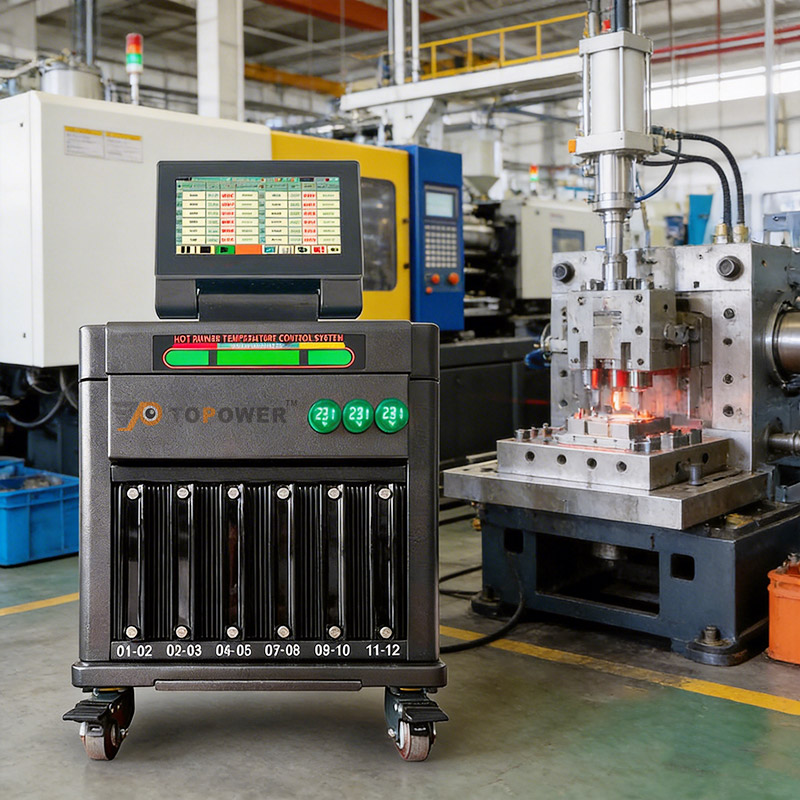
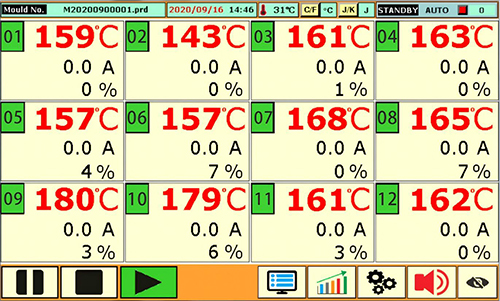
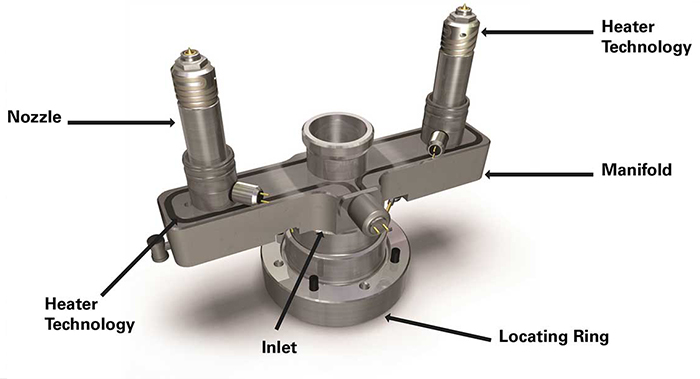
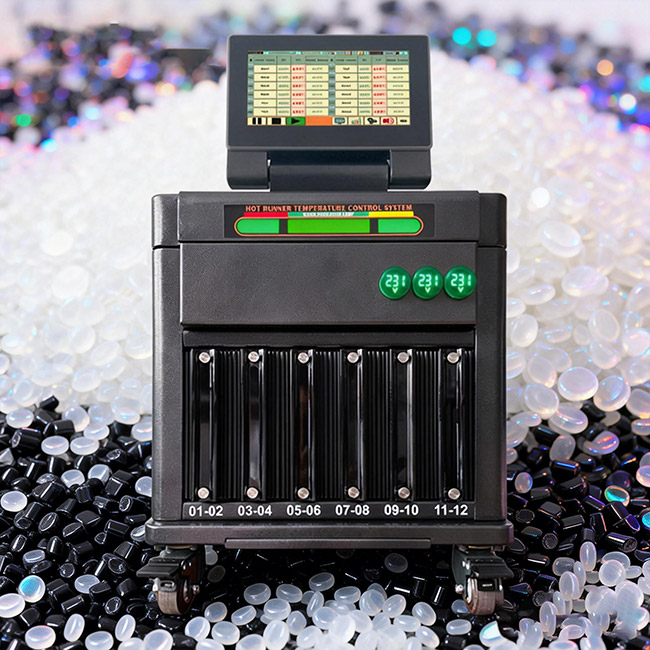
In modern injection molding, precision is not optional—it is fundamental. At the center of th...
Applications of Hot Runner Temperature Controllers for Different Plastic Materials
In plastic injection molding, accurate and stable temperature control plays a critical role in product quality, cycle time, and mold lifespan. As the core component of a hot runner system, a hot runner temperature controller must be precisely matched to the processing characteristics of different plastic materials.
Each plastic resin has its own melting temperature range, thermal stability, and sensitivity to temperature fluctuations. Therefore, understanding how hot runner temperature controllers perform with different materials is essential for engineers, mold designers, and procurement professionals.
This article explores the applications of hot runner temperature controllers across common injection molding materials, highlighting key control requirements and selection considerations.

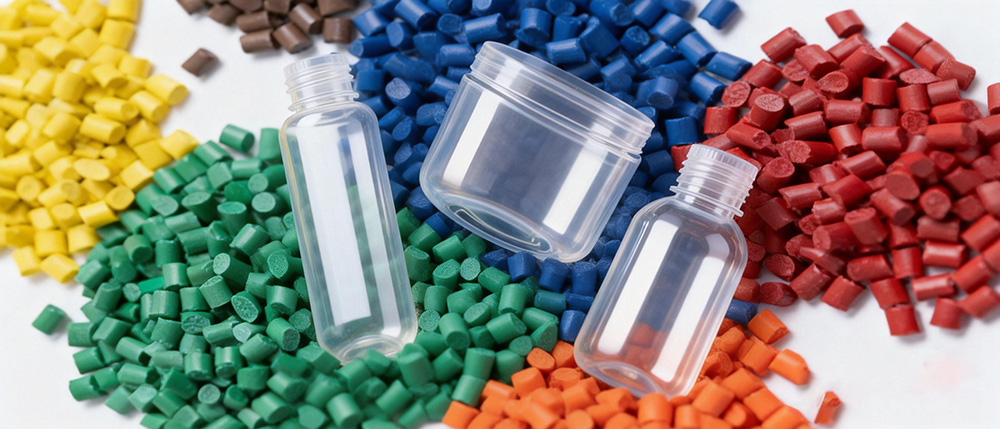
Why Different Materials Require Different Temperature Control
Plastic materials vary significantly in:
Melting temperature range
Thermal stability
Sensitivity to shear and overheating
Crystalline or amorphous structure
Tolerance to temperature fluctuation
Using the same temperature control strategy for all materials often leads to issues such as:
Stringing and drooling
Material degradation or burning
Short shots or uneven filling
Poor surface finish and inconsistent mechanical properties
This is why high-precision, multi-zone hot runner temperature controllers have become standard in modern injection molding.
Applications of Hot Runner Temperature Controllers by Material Type
PP and PE (Polypropylene & Polyethylene)
Material Characteristics
Low melting temperature
Good thermal stability
Relatively tolerant to temperature variation
Temperature Control Requirements
Focus on overall temperature stability
Prevent overheating that may cause drooling
Even temperature ramp-up during startup
Recommended Controller Features
Standard PID temperature control
Single-zone or basic multi-zone controllers
Moderate response speed
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
Material Characteristics
Moderate thermal stability
Sensitive to overheating
High surface quality requirements
Temperature Control Requirements
Tight control of temperature differences between manifold and nozzles
Avoid localized overheating to prevent discoloration or burn marks
Minimize temperature fluctuation during production
Recommended Controller Features
High-accuracy PID control
Real-time temperature monitoring and alarm functions
Soft start function to protect heaters
PC (Polycarbonate)
Material Characteristics
High processing temperature
High melt viscosity
Extremely sensitive to temperature stability
Temperature Control Requirements
Insufficient temperature causes short shots
Excessive temperature leads to material degradation
Precise multi-zone synchronization is critical
Recommended Controller Features
High power output capability
Accurate multi-zone temperature control
Thermocouple break detection and rapid fault protection
PA / Nylon (Including Glass-Filled Grades)
Material Characteristics
Hygroscopic material
Glass fiber significantly affects flow behavior
Sensitive to both shear and temperature
Temperature Control Requirements
Accurate nozzle temperature control to reduce stringing
Independent adjustment for different heating zones
Fast temperature response to process changes
Recommended Controller Features
Multi-zone independent control (8, 16 zones or more)
Fast-response control algorithms
Designed for continuous high-load operation
PET, PBT and Other Engineering Plastics
Material Characteristics
Narrow processing temperature window
Crystallization behavior is highly dependent on temperature
High dimensional stability requirements
Temperature Control Requirements
Long-term stable temperature control
Extremely small temperature deviation between zones
Prevent temperature drift that affects part dimensions
Recommended Controller Features
Industrial-grade high-stability temperature controllers
Real-time monitoring with data logging capability
Communication interfaces for system integration

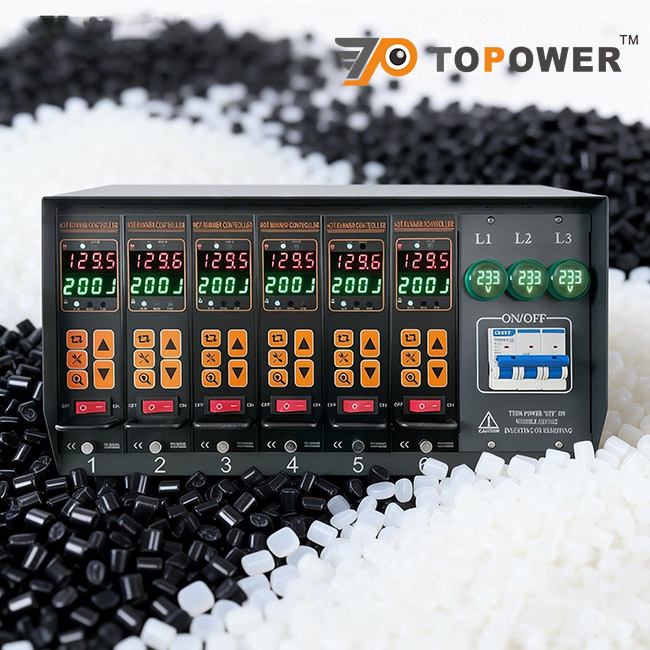
Advantages of Multi-Zone Hot Runner Temperature Controllers
As mold designs become more complex, single-zone control is no longer sufficient. Multi-zone hot runner temperature controllers offer clear advantages:
Independent control of each nozzle and heating zone
Reduced temperature deviation across the hot runner system
Improved part consistency and surface quality
Lower scrap rate and reduced setup time
These benefits are significant in automotive, electronics, medical, and packaging applications.
How to Select the Right Hot Runner Temperature Controller
When choosing a hot runner temperature controller, consider the following factors:
Temperature control accuracy (±0.1°C or ±0.5°C)
Number of control zones (6–120 zones)
Output power and load capacity
Safety protections (over-temperature, short circuit, thermocouple failure)
User interface (modular controller or touchscreen controller)
The more temperature-sensitive the material, the higher the performance requirements for the controller.
Conclusion
Different plastic materials place very different demands on hot runner temperature control. Selecting a hot runner temperature controller that matches the material’s processing characteristics is essential for achieving stable production, consistent part quality, and long-term mold reliability.
As injection molding continues to move toward higher precision and automation, high-accuracy, intelligent, multi-zone hot runner temperature controllers will remain a key foundation for advanced manufacturing.