Contents1. Why cold runners drive waste in medical molding2. Eliminating Cold Runner Waste with hot ...
Injection Mold Maintenance and Care
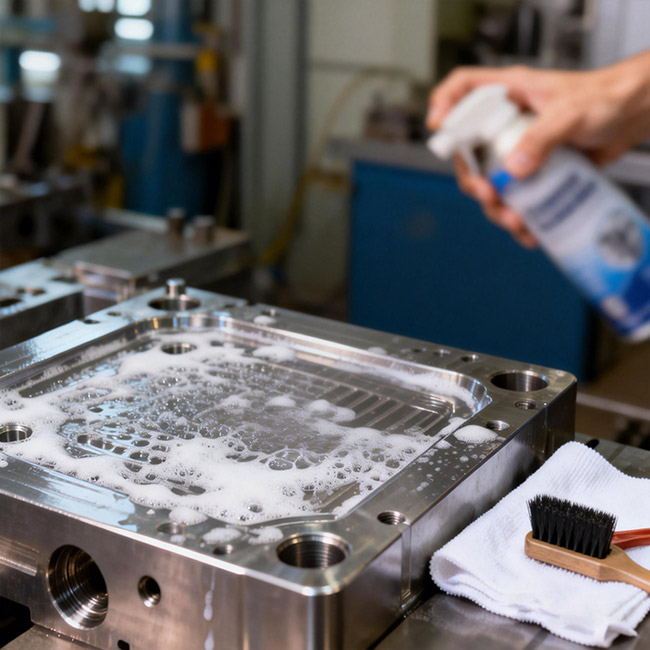

Key Practices to Extend Mold Life and Ensure Stable Production
Injection molds are core production assets in plastic injection molding. Their condition directly affects product quality, production efficiency, and overall manufacturing cost. In most injection molding facilities, molds are frequently changed due to diversified product lines and short production cycles. After each production run, molds are typically removed from the machine and stored until the next use.
Without systematic maintenance and proper storage, molds are prone to corrosion, surface degradation, and mechanical wear during idle periods. These issues can lead to dimensional instability, surface defects, increased scrap rates, and, in severe cases, premature mold failure that requires costly replacement. Therefore, professional mold maintenance is essential for sustainable and cost-effective manufacturing.
Industry data indicates that usage and maintenance account for approximately 15%–20% of the factors affecting mold service life. Under proper operating and maintenance conditions, injection molds commonly achieve a service life of around 800,000 cycles, while well-maintained molds can last significantly longer. Poor maintenance practices, however, can reduce mold life dramatically and increase material waste, energy consumption, and production downtime.
Why Injection Mold Maintenance Is Critical
Injection molds consist of complex structures and numerous precision components. Any degradation in critical parts can disrupt production and compromise product quality. A structured mold maintenance program helps manufacturers:
Extend mold service life
Reduce unplanned downtime
Maintain consistent product quality
Lower total operating and capital costs
Establishing a Mold History and Tracking System
A comprehensive mold history record should be created for every injection mold. This record provides full lifecycle visibility and supports preventive maintenance planning.
Recommended Mold History Contents
Mold identification and total shot count
Production cycle records
Maintenance and repair history
Replaced components and failure causes
Key molding process parameters
Resin types and product applications
Analyzing historical data enables engineers to identify wear trends, predict failures, and reduce setup and trial times during subsequent production runs.
Mold Performance Evaluation During Production
While the mold and injection molding machine are operating under normal conditions, mold performance should be continuously assessed. This includes measuring critical dimensions and inspecting the appearance of the final molded parts.
Key Areas to Monitor
Cavity and core wear or deformation
Parting line alignment and sealing condition
Cooling efficiency and cycle time stability
Defects observed in molded parts often provide early indications of mold degradation, allowing corrective actions before major failures occur.
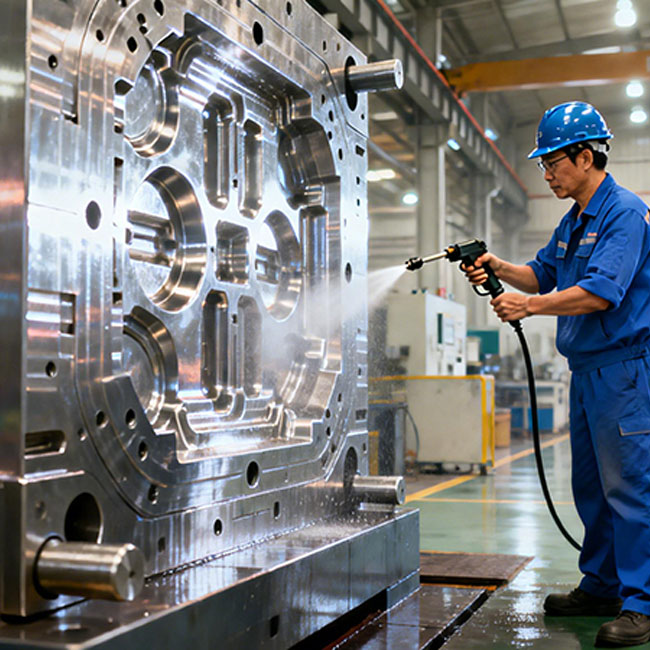

Maintenance of Critical Mold Components
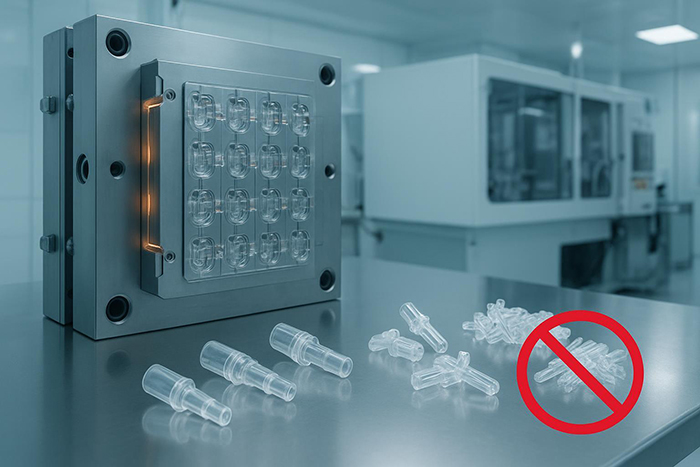
injection and Guiding Systems
Ejector pins, guide pillars, and guide bushings ensure smooth mold opening, closing, and part ejection. Deformation, wear, or seizure of these components can cause immediate production stoppage. Regular inspection and timely replacement are essential.
Moving and Transmission Components
Sliding cores, gears, racks, bearings, and springs should be cleaned, lubricated, and protected after each production cycle. Spring force degradation should be monitored to maintain consistent mold operation.
Cooling System Cleaning and Maintenance
The cooling system plays a critical role in cycle time control and part quality. Over time, cooling channels may accumulate scale, rust, sludge, or biological deposits, reducing flow rate and heat transfer efficiency.
Best Practices
Periodic inspection and flushing of cooling channels
Use of appropriate descaling or cleaning methods
Monitoring cooling performance trends
Proper cooling system maintenance helps maintain stable cycle times and reduces energy consumption.
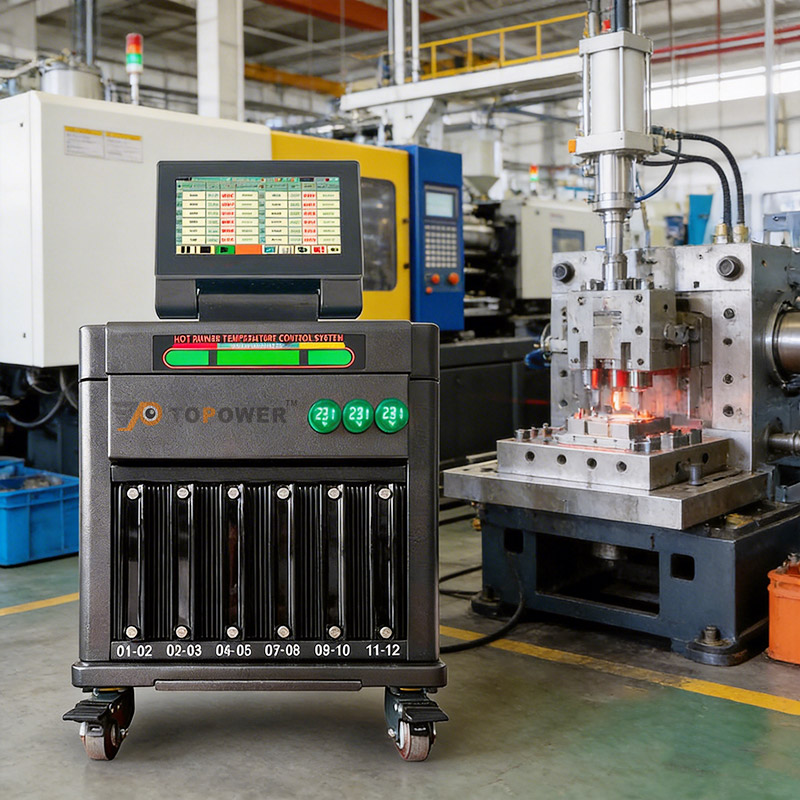
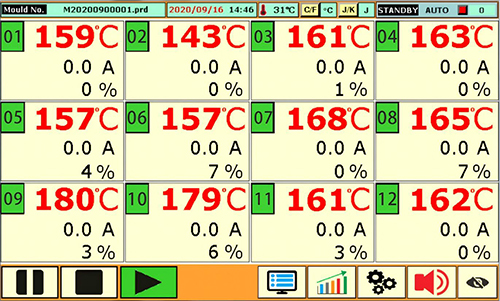
Maintenance of Hot Runner Heating and Control Systems
For hot runner molds, stable heating and temperature control are essential to avoid production defects and downtime.
Components to Inspect After Each Production Cycle
Band heaters and cartridge heaters
Heating probes
Thermocouples and wiring connections
Electrical resistance and continuity should be checked using appropriate measuring tools. Any abnormal readings should be recorded and addressed immediately.
Coordinated Maintenance Between Mold and Temperature Control System
To achieve optimal performance, maintenance activities should address both the mold hardware and the temperature control system in parallel:
Regular electrical resistance and insulation checks of band heaters and cartridge heaters
Periodic verification of thermocouple accuracy and signal stability
Inspection of connector integrity, wiring strain relief, and grounding
Cross-checking actual melt temperature trends against controller setpoints
Any abnormal temperature fluctuation should trigger not only electrical inspection but also mechanical evaluation of the hot runner manifold, nozzles, and flow channels.
Mold Surface Cleaning and Corrosion Protection
Mold surface condition directly affects the appearance of molded products. After production, residual plastic and deposits should be carefully removed using soft tools such as copper rods, copper brushes, or mild cleaning agents.
Important Guidelines
Avoid steel wires or hard tools that may scratch mold surfaces
Polish corrosion spots caused by aggressive resins
Apply rust preventive oil after cleaning
Store molds in dry, clean, and dust-free environments
Benefits of Proper Injection Mold Maintenance
A well-maintained injection mold delivers long-term operational and financial benefits:
Extended mold lifespan
Reduced setup and troubleshooting time
Improved product consistency
Lower scrap and defect rates
Reduced maintenance and replacement costs
Summary
Effective injection mold maintenance is a fundamental engineering practice that directly influences process stability, product consistency, and equipment longevity. When maintenance activities are systematically planned and coordinated with hot runner temperature control systems, molds operate under more predictable thermal and mechanical conditions. This integrated approach enables early detection of deviations, reduces the risk of unexpected failures, and supports repeatable molding performance across production cycles. In the long term, engineering-driven maintenance strategies provide a reliable foundation for stable manufacturing, quality assurance, and sustainable operational efficiency.