The Ultimate Guide to Valve Gate Injection Molding Techniques
2025-05-21
Valve gate injection molding is a specialized technique in plastic injection molding that provides enhanced control, efficiency, and quality in the production of molded parts. Whether you are a mold designer, process engineer, or production manager, understanding valve gate systems can significantly improve your product's aesthetics and performance while reducing waste and cycle times.
This ultimate guide covers the principles, benefits, components, techniques, applications, and best practices of valve gate injection molding.
What is Valve Gate Injection Molding?
Valve gate injection molding is a hot runner system that uses mechanical or hydraulic/pneumatic pins (valves) to open and close the gate through which molten plastic flows into the mold cavity. Unlike traditional open hot tip systems, valve gate systems precisely control the timing and flow of plastic, enabling better part quality and performance.
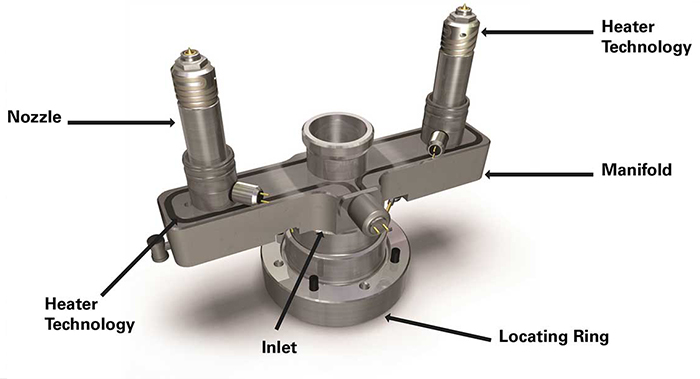
Key Components of a Valve Gate System
Valve Pin (or Needle): Moves up and down to open or close the gate.
Actuator: Operates the pin using pneumatic, hydraulic, or electric mechanisms.
Nozzle Tip: Directs molten plastic into the cavity and interfaces with the mold.
Gate (Orifice): The entry point into the mold cavity, controlled by the valve pin.
Hot Runner Manifold: Channels that maintain molten plastic at a consistent temperature across multiple cavities.
| Valve Gate vs. Open Gate Systems |
|
|
|
| Feature | Valve Gate System | Open Gate (Hot Tip) System |
| Gate Control | Active (via pin) | Passive (free flow) |
| Cosmetic Finish | Superior (no gate vestige) | May leave marks |
| Cycle Time | Shorter | Often longer |
| Material Waste | Reduced | Can be higher |
| Multi-cavity Control | Excellent | Less precise |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower |
Benefits of Valve Gate Injection Molding
Improved Surface Finish: No gate vestige on parts, ideal for cosmetic components.
Cycle Time Reduction: Faster fill and cooling cycles due to better gate control.
Material Savings: Minimizes stringing, drool, and overpacking.
Precise Fill Control: Excellent for sequential filling and large, complex parts.
Flash Elimination: Reduces risk of flashing from uncontrolled flow.
Improved Weld Line Strength: Sequential gating can move weld lines to less critical areas.
Techniques & Strategies
1. Sequential Valve Gating
Used to fill large or complex parts in stages to avoid weld lines and improve flow. Each gate opens and closes at precise times based on part geometry and mold fill analysis.
Applications: Bumpers, automotive panels, appliance housings.
2. Simultaneous Valve Gating
All gates open at once, useful for symmetrical multi-cavity molds or when simultaneous fill is critical.
Applications: Closures, caps, packaging components.
3. Cascade Molding
A variation of sequential gating where the gates open progressively along the flow path to reduce weld lines and maintain consistent pressure.
Applications of Valve Gate Molding
Automotive: Fascias, grilles, interior panels.
Medical Devices: Diagnostic equipment, surgical tools.
Consumer Electronics: Casings, bezels, connectors.
Packaging: Thin-wall containers, closures.
Large Structural Parts: Bins, crates, appliance housings.
Common Challenges & Troubleshooting
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|
| Stringing/Drool | Incomplete valve closure | Check valve timing and pin seal |
| Flashing | Excessive pressure or worn pin | Optimize pressure and inspect components |
| Sink Marks | Poor packing | Adjust fill speed or gate close timing |
| Jetting | Early gate opening | Delay gate activation or increase back pressure |
| Incomplete Fill | Late gate opening or undersized gate | Review gate design and timing |
Best Practices
Use Mold Flow Analysis: Simulate valve gate behavior before tool build.
Ensure Precise Timing Control: Use high-quality controllers and actuators.
Design Gates Appropriately: Gate size, shape, and location affect flow and quality.
Perform Regular Maintenance: Prevent leaks, wear, and misalignment.
Document & Optimize Parameters: Keep a detailed log for each mold and part.
Future Trends in Valve Gate Technology
Electric Actuation: Greater precision, cleaner operation, and faster response.
Smart Sensors: Real-time monitoring of pin position, pressure, and temperature.
AI-Driven Optimization: Using machine learning to predict gate timing and detect defects.
Sustainable Design: Systems that reduce material use and enable recyclability.
Conclusion
Valve gate injection molding is a powerful tool in the hands of engineers and manufacturers aiming for precision, quality, and efficiency. While the initial cost may be higher than traditional systems, the long-term benefits—especially for high-volume, complex, or cosmetic parts—are undeniable.
By mastering valve gate techniques and adopting the latest advancements, manufacturers can stay ahead in a competitive market while improving sustainability and product integrity.