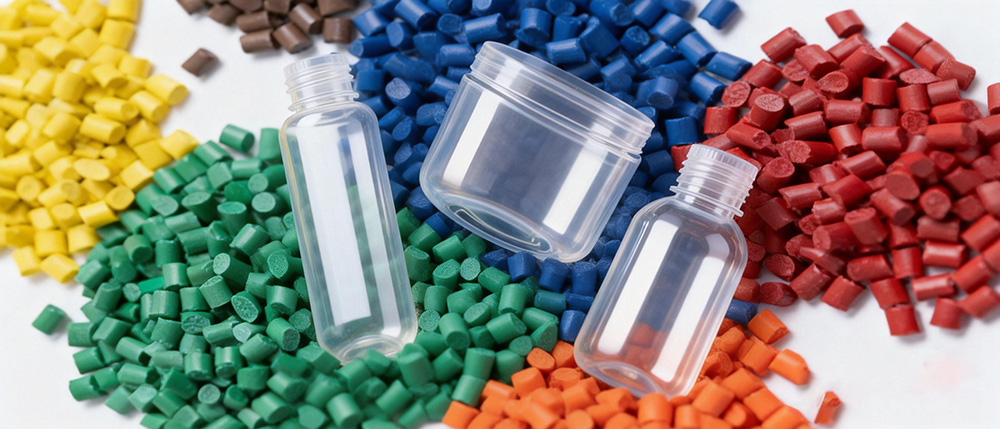
Everyday Plastic You Encounter — But Do You Really Understand It?Have you ever noticed a small tria...
Injection Molding: Turning Ideas into Millions of Products

What is Injection Molding?
Injection molding is an advanced manufacturing process in which plastic is melted, injected under high pressure into a precision mold, cooled, and solidified into a finished part. This technology combines material science, mechanical engineering, and precision tooling, making it one of the most efficient and reliable forming methods in today’s plastics industry.
Compared with additive manufacturing technologies such as 3D printing, the biggest advantage of injection molding lies in its ability to produce high volumes at low cost. A single precision mold can continuously produce hundreds of thousands to millions of parts with consistent dimensions and performance. As output increases, the cost per part drops significantly. This is why industries such as automotive, electronics, medical, and consumer goods rely on it as their go-to manufacturing method.
Three Core Elements of Injection Molding
Material Science: Precise Resin Selection
Injection molding materials generally fall into three categories:
General-purpose plastics (PP, PE): good toughness and chemical resistance, widely used in packaging and containers.
Engineering plastics (ABS, PC, PA): excellent strength and heat resistance, ideal for structural components and housings.
High-performance plastics (PEEK, PPS): outstanding thermal stability and mechanical performance, used in aerospace and medical applications.
For hygroscopic materials such as PC and PA, strict drying (moisture content ≤0.02%) is required to ensure quality and avoid defects like bubbles or silver streaks.
Precision Equipment: Injection Machines and Mold Systems
The injection molding machine is the heart of the process, consisting of:
Injection system: heats, melts, measures, and injects the plastic.
Clamping system: provides sufficient clamping force to keep the mold closed under high pressure.
The mold is the “soul” of injection molding, directly determining product quality. Modern molds adopt modular designs and integrate:
Forming systems (cavity and core)
Runner systems (guiding the melt)
Temperature control systems
Ejection systems for automatic part removal
Process Control: Accuracy in Every Stage
From raw material preparation to final molding, every step requires strict control:
Temperature management (optimized heating curves for different plastics)
Pressure regulation (injection and holding pressure)
Time control (precisely managed cycle times)
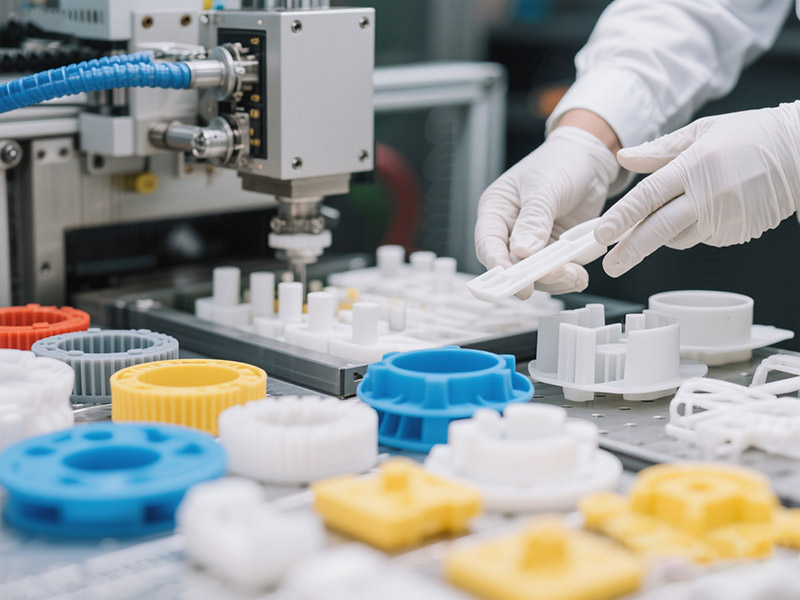

Four Key Stages of Injection Molding
Melting & Preparation
Plastic pellets are dried and blended, then fed into the injection barrel. Under heating and screw shear, solid pellets transform into a uniform molten state.
Injection & Filling
The molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity at preset speed and pressure. Proper control of injection velocity, pressure, and temperature ensures complete filling.
Packing & Cooling
Holding pressure compensates for material shrinkage, preventing voids or sink marks. Cooling channels in the mold quickly remove heat, solidifying the part.
Ejection & Post-Processing
After sufficient cooling, the mold opens, and ejector pins push the part out. Robotic systems may handle trimming, inspection, and other secondary operations.
Technical Advantages of Injection Molding
High efficiency: cycle times as short as 3–5 seconds; multi-cavity molds enable daily output in the millions.
Dimensional precision: tolerances up to ±0.02 mm for demanding applications.
Complex geometries: undercuts, threads, thin walls, and intricate features formed in one cycle.
Superior surface finish: A-class surface quality directly from the mold.
High material utilization: runners and waste can be recycled, with material efficiency exceeding 95%.
Applications Across Industries
Automotive: dashboards, bumpers, interior components
Electronics: phone housings, connectors, insulators
Medical: syringes, IV sets, surgical instruments
Consumer goods: packaging, home products, toys
Industrial components: gears, bearings, housings
Future Trends
With the rise of Industry 4.0, injection molding is rapidly evolving toward intelligent and sustainable manufacturing:
Smart injection systems: AI-driven process optimization and adaptive control
Micro-injection molding: for MEMS and miniature medical devices
Green manufacturing: bioplastics, recycling, and reduced environmental impact
Multi-material molding: integrating hard/soft plastics and multiple colors in a single process
Conclusion
As a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, injection molding not only delivers unmatched efficiency and cost advantages but also drives continuous product innovation. From everyday items to high-tech devices, this process silently supports the growth of modern society. With ongoing advances in materials and technologies, injection molding will continue to play a vital role in shaping the future of manufacturing.