Everyday Plastic You Encounter — But Do You Really Understand It?Have you ever noticed a small tria...
A Guide to Choosing Precision Temperature Controllers for Industrial Use

Precision temperature controllers are important for industrial work. They keep temperatures steady and accurate, helping products stay good and machines run smoothly. These systems stop equipment from breaking and save time, making work more efficient.
Safety is very important in factories, and these controllers help a lot. They:
Keep temperatures steady to stop big changes.
Have alarms to warn about problems.
Turn off machines to stop overheating or freezing.
By solving these problems, precision controllers help machines work well and keep workers safe.
Key Takeaways
Precision temperature controllers keep temperatures steady, improving quality and efficiency.
Use ON-OFF controllers for easy tasks and to save money. Choose PID controllers for harder jobs needing more accuracy.
PID control saves energy and stays stable, great for food and medical industries.
Check for features like autotuning and communication tools to improve use and connect to systems.
Think about your industry needs to pick the right controller for best results and safety rules.
Types of Precision Temperature Controllers

Precision temperature controllers come in various types. Each type is made for specific industrial tasks. Knowing these types helps you pick the best one.
ON-OFF Controllers
ON-OFF controllers are the easiest to use. They turn heating or cooling devices on when the temperature is too low. They turn them off when the temperature gets too high. This simple method makes them dependable and cheap.
But ON-OFF controllers might not be precise enough for complex jobs. They can cause temperature swings, called overshoot and undershoot. These swings can hurt product quality or machine performance. Still, ON-OFF controllers work well for jobs where exact temperature control isn’t needed.
Tip: Choose ON-OFF controllers for simple systems that need to save money.
PID Controllers
PID controllers are more advanced. They use three parts: proportional, integral, and derivative. These parts work together to keep the temperature steady. PID controllers adjust constantly to match the desired temperature. This gives smoother and more accurate control.
Industries like medical equipment and food processing need PID controllers. They save energy, improve product quality, and make processes more stable.
Controller Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
ON-OFF Controller | Easy to use, reliable, affordable | Less precise, causes wear, noisy |
PID Controller | N/A |
Key Differences Between ON-OFF and PID Controllers
ON-OFF and PID controllers have clear differences. ON-OFF controllers are simple and cheap but less accurate. PID controllers give better control and are good for tough industrial tasks.
Precision: PID controllers keep temperatures steady with fewer swings. ON-OFF controllers may cause overshoot and undershoot.
Energy Efficiency: PID controllers save energy and lower costs. ON-OFF controllers switch often and waste energy.
Application: Use ON-OFF controllers for basic tasks. Use PID controllers for jobs needing high accuracy.
Studies show fuzzy logic controllers are even better. They save 30-70% energy in buildings while keeping temperatures comfortable. Picking the right controller depends on your needs.
Understanding PID Control in Precision Temperature Controllers
PID control is a smart way to keep temperatures steady. It uses three parts—proportional, integral, and derivative—to adjust the system. These parts work together to keep the temperature at the right level.
Proportional Component
The proportional part fixes errors by reacting to the current difference. This difference is between the set temperature and the actual one. Bigger errors mean stronger fixes, while smaller errors need lighter changes.
Key Features:
Reacts quickly to changes.
Reduces delays in system adjustments.
Works best with the other two parts.
Effect on Temperature | Notes | |
|---|---|---|
45% of Setpoint | Quick response | Too much can cause overshoot |
70% of Setpoint | Balanced response | High settings may cause cycling |
This part helps keep temperatures steady in real-time. It’s great for places needing fast adjustments.
Integral Component
The integral part fixes leftover errors over time. It looks at past errors and adjusts to fix any small differences. Even if there’s no current error, it keeps the temperature steady.
This is helpful for jobs needing long-term accuracy. Higher integral settings fix errors faster but can cause wobbling around the setpoint.
Note: The integral part is key for systems needing steady and exact temperatures.
Derivative Component
The derivative part predicts future errors by watching how fast things change. It slows down big swings and keeps the system steady.
Key Benefits:
Reacts to quick temperature changes.
Keeps the system from wobbling too much.
Helps in places with sudden temperature shifts.
Effect on System Response | |
|---|---|
Small Td | Stable, less noise |
Large Td | Faster, but may wobble |
This part is useful where quick temperature changes can hurt products or machines.
These three parts work together to make PID control effective. They help precision controllers work well in many different industries.
Advantages of PID Control in Industrial Settings
PID control has many benefits for factories and industries. It keeps temperatures steady, which helps products stay good and machines work well. By adjusting all the time, PID controllers make sure your systems run smoothly.
One big advantage is its accuracy. Unlike basic on/off controllers, PID controllers stop big temperature changes. This prevents overheating or freezing, which is very important for food and medical industries. Even small temperature changes can cause problems. PID controllers also save energy. They make small adjustments to avoid wasting power, which lowers costs.
PID control is very flexible. You can use it in analog, digital, or mechanical systems. This makes it easy to fit into different setups without big changes. It also helps machines last longer by stopping constant on/off switching, which wears them out.
For over 70 years, PID control has been trusted in factories. Engineers have made it better over time, proving it works well. While newer methods like Fuzzy Logic Control are good for special tasks, PID control is still the best choice for simple jobs because it’s easy to use and adjust.
Advanced Features in Precision Temperature Controllers
Autotuning Capabilities
Autotuning makes temperature control easier by adjusting settings automatically. This saves time and avoids mistakes since you don’t have to change settings yourself. It helps the controller adapt to changes, keeping performance steady even when loads vary.
With autotuning, products turn out better because temperatures stay controlled. For instance, in factories, better control means fewer mistakes and higher quality. It also uses energy wisely, cutting costs and boosting efficiency.
Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
Auto-tuning | Saves time by removing the need for manual changes. |
Rapid response time | Makes quick adjustments for better temperature control. |
Adaptability | Keeps performance steady during big load changes. |
Improved product quality | Leads to fewer defects and better results in production. |
Reduced energy consumption | Saves energy by optimizing temperature processes. |
Tip: Choose autotuning for tasks needing accuracy and dependability.
Communication Protocols for Enhanced Integration
Modern communication protocols help connect temperature controllers to other systems. They allow data sharing, making work smoother and letting you monitor remotely.
Some common protocols are Modbus, OPC-UA, Ethernet/IP, and Profinet. Modbus works fast, great for quick actions. OPC-UA handles long distances, good for big networks. Ethernet/IP and Profinet send data quickly and reliably.
Key Benefits of Communication Protocols:
Help machines and systems work together easily.
Support smart controls with IoT technology.
Allow AI tools to predict and fix problems early.
Using these protocols improves system connections and simplifies operations.
Multi-zone Temperature Control
Multi-zone control lets you manage different areas separately in one system. This is important for jobs needing precise heat in specific spots.
For example, in fluidized bed reactors, it ensures even heat for chemical reactions. In glass-making, it keeps work going even if a heater is replaced. This feature saves time and boosts efficiency.
Application Type | Description | Benefits of Multi-Zone Temperature Control |
|---|---|---|
Fluidized Bed Reactors | Heats gases at high temperatures. | Ensures even heat and accurate control. |
Clean Burning Coal Processes | Removes harmful stuff from coal. | Meets EPA rules affordably. |
Super Plastic Forming | Shapes metals like titanium and aluminum. | Helps make jet engine parts precisely. |
Soil Remediation | Cleans polluted soil. | Removes harmful chemicals effectively. |
Aluminum Extruding | Uses heaters for better heating. | Cuts downtime and improves heat use. |
Architectural Glass Production | Uses zones for shaping glass. | Keeps work going during heater changes. |
Multi-zone control works best for industries needing accurate heat control in many areas.
Alarm and Safety Features
Alarm and safety features are very important in temperature controllers. They keep machines safe and protect workers by spotting temperature problems. These features act as the first defense against overheating or freezing.
Main Jobs of Alarm Systems
Modern controllers have alarms to warn about temperature issues. Sensors check for changes and send alerts right away. Some alarms make loud sounds, while others flash lights.
Spotting Temperature Problems: Warns if the temperature is too high or low.
System Error Alerts: Tells you if sensors or circuits stop working.
Emergency Stop: Shuts down machines to avoid damage or danger.
Tip: Test alarms often to make sure they work in emergencies.
Making Systems Better with Predictions
Advanced alarms use smart models to predict problems early. These models study temperature patterns to stop issues before they happen. For example, fire alarms use these models to work better.
Project Task | Goal |
|---|---|
Study smoke patterns | Improve how detectors respond to smoke. |
Build smart prediction models | Make alarms better with advanced designs. |
Check fire alarm system reliability | See how changes affect system performance. |
These updates cut down false alarms and make systems more reliable. This helps work go on without interruptions.
Why Alarm and Safety Features Matter
Alarms save machines and protect lives. They stop problems early, avoiding costly delays. They also help follow safety rules, lowering the chance of fines.
Adding alarms and safety features to controllers makes work safer and smoother.
Picking the Best Precision Temperature Controller
Choosing the right precision temperature controller can improve how your factory works. By knowing what you need and checking key points, you can pick one that works well, stays accurate, and is reliable.
Things to Think About (e.g., Job Type, Accuracy Needs)
When picking a precision temperature controller, think about these important points. They help make sure the controller fits your needs and works its best.
Job Type: Different jobs need different temperature controls. For example, food factories need steady temperatures to keep food safe. Medical tools need exact control for accurate results.
Accuracy Needs: Some jobs need very precise temperatures. For example, making computer chips needs controllers that keep temperatures steady without big changes.
Workplace Conditions: Things like humidity, dust, or extreme heat can affect how the controller works. Pick one made for your workplace to make sure it lasts and works well.
Easy to Connect: Many modern controllers can connect to other systems using tools like Modbus or Ethernet/IP. This makes them work better with your current setup.
Safety Features: Alarms, emergency stops, and tools that predict problems are important. They help avoid accidents and keep work running smoothly.
Using expert advice and research helps you make a smart choice. By thinking about these points, you can pick a controller that matches your goals.
Suggestions for Different Industries (e.g., Food, Medical Tools)
Not all precision temperature controllers are the same. Each industry has special needs, so you should pick a controller that fits your job.
Food Factories: Keeping steady temperatures is key for food safety and quality. PID controllers with features like autotuning and multi-zone control work best here.
Medical Tools: Medical devices need exact temperature control for safety and accuracy. Controllers with fast responses and strong safety features are a must.
Plastic Making: Jobs like injection molding need controllers with multi-zone control. These keep temperatures even, improving product quality and cutting down on mistakes.
Farming: Greenhouses and animal shelters need controllers that adjust to changing weather. Controllers with remote monitoring and communication tools work great here.
By choosing a controller that fits your industry, you can get better results and work more efficiently.
Balancing Cost and Quality
Finding a balance between cost and quality is important when picking a precision temperature controller. Fancy controllers with many features might not always be needed.
Know What You Need: List the features your job requires. For simple tasks, an ON-OFF controller might be enough and save money. For harder jobs, a PID controller with extra features is worth the price.
Think About Future Savings: High-quality controllers may cost more upfront but save money later. They use less energy, reduce downtime, and last longer, making them a good investment.
Check Compatibility: Make sure the controller works with your current systems. This avoids extra costs for changes or new equipment.
Compare Options: Look at different brands and models to find the best deal. Read reviews and ask experts for advice to make a smart choice.
By thinking about your needs and both short-term and long-term costs, you can pick a controller that works well and fits your budget.
Top Brands and Models to Consider
Picking the right brand and model is important. It ensures your precision temperature controller works well and lasts long. The market for these controllers is growing fast. By 2032, it may reach $1.73 billion, up from $900 million in 2023. Many industries, like food, medicine, and energy, depend on these devices to meet strict rules. Below are some trusted brands and models for industrial use:
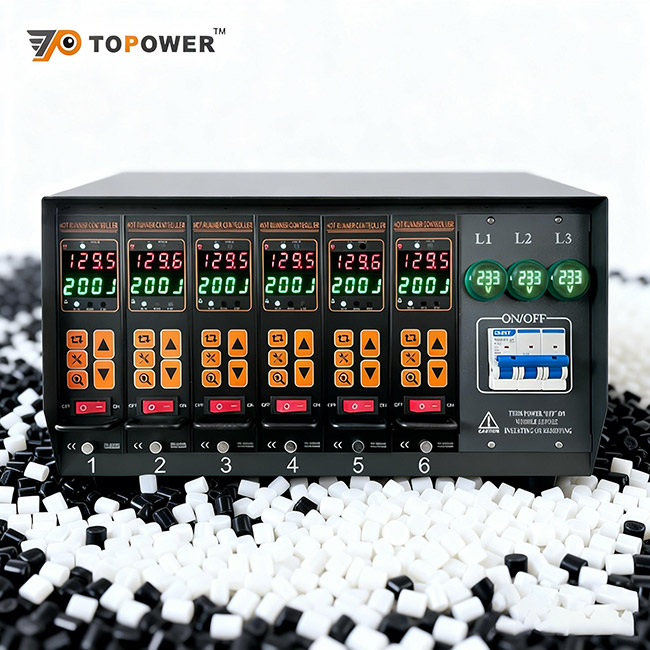
TOPOWER HY20 Touch screen Hot runner Temperature controler
This controller keeps temperatures steady with smart features. soft-start functions, and manual controls for sensor issues. It works with brands like DME and YUDO, making it useful for farming, medical tools, and smart homes.Omron E5CC Series
The E5CC series is small and easy to use. It controls temperatures accurately using PID technology. It supports many communication tools, making it great for modern factories.Honeywell UDC3200 Universal Controller
This model offers strong performance with autotuning and multi-zone control. Its tough design works well in hard conditions, like power plants and chemical factories.Watlow EZ-ZONE PM Controller
The EZ-ZONE PM series is flexible and precise. It has alarms, remote monitoring, and energy-saving options. It’s perfect for jobs needing multi-zone control, like plastic and glass-making.Eurotherm 3200 Series
The 3200 series is simple and efficient. It uses PID control and meets strict industry rules. It’s ideal for food factories and medicine production.
When choosing a controller, think about your job needs, accuracy, and workplace conditions. A good model from a trusted brand can save money and improve efficiency.
Tip: Make sure the controller works with your current systems and supports your communication tools.
Precision temperature controllers are important for factories and industries. They help keep products good, make work faster, and keep workers safe. As machines get smarter and factories grow, these controllers are used more often.
Market Insights:
The global market for PID temperature controllers may grow from $1.2 billion in 2023 to $2.1 billion by 2032.
This shows how useful precise temperature control is for cutting waste and keeping product quality steady.
When picking a controller, think about your job needs, how accurate it must be, and if it works with your current systems. Trusted brands and expert tips can help you choose the right one for your work.
FAQ
What does a precision temperature controller do?
It keeps the temperature within a set range. This helps machines work well and improves product quality in factories.
How do you pick between ON-OFF and PID controllers?
Use ON-OFF controllers for simple jobs that don’t need high accuracy. Pick PID controllers for tasks needing steady and exact temperature control.
Can these controllers help save energy?
Yes, they can. PID controllers adjust temperatures smartly to avoid wasting energy. Features like autotuning also help save power.
Do precision temperature controllers work with all systems?
Most modern controllers use common tools like Modbus or Ethernet/IP. These tools help them connect with many systems. Always check if it fits your setup.
Which industries use precision temperature controllers the most?
Industries like food, medical tools, plastics, and farming use them a lot. They help keep temperatures safe and accurate for better results.
Tip: Choose a controller with features that match your industry’s needs.